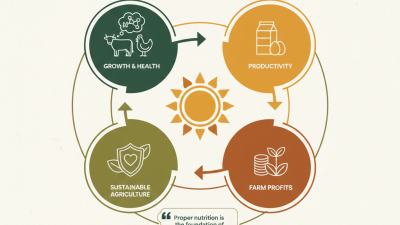
Live stock plays a crucial role in agriculture. These are animals raised for food, fiber, and other products. Farmers rely on live stock for various reasons. They provide essential nutrients, such as meat, milk, and eggs. This supports both local and global food supply.
The importance of live stock extends beyond mere food production. They contribute to soil fertility through manure. Additionally, they help create biodiversity on farms. This diversity can lead to more resilient ecosystems, benefiting crops and other wildlife.
However, the challenges surrounding live stock management cannot be ignored. Issues like animal welfare and environmental impact arise frequently. Farmers must continuously reflect on these challenges to find better practices. Balancing productivity with ethical responsibilities is not easy. Yet, addressing these matters is vital for sustainable agriculture.
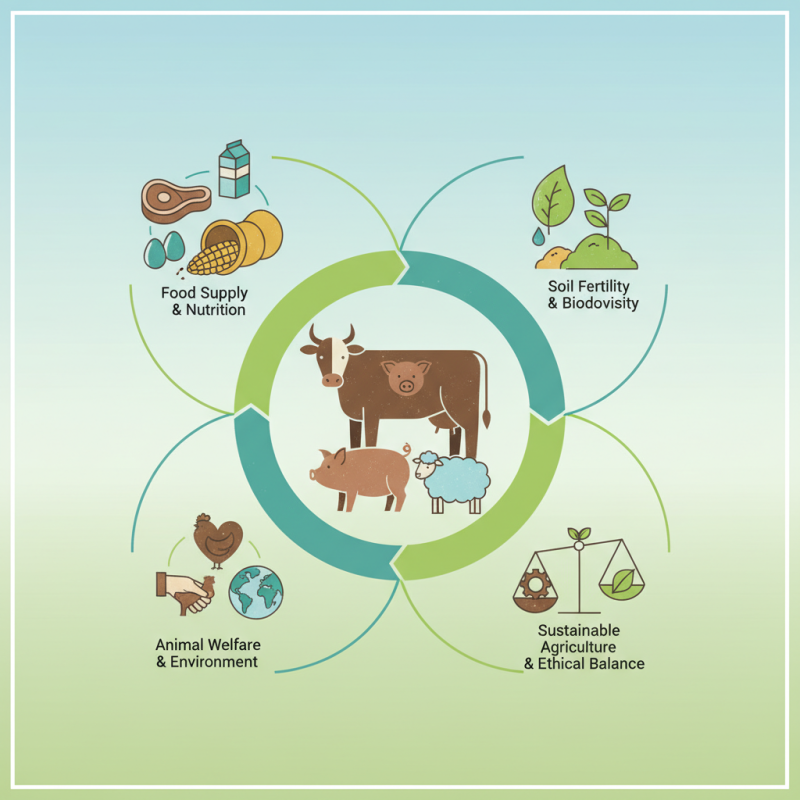

Livestock are domesticated animals raised for food, fiber, and other products. They include cows, pigs, sheep, goats, and chickens. Each type of livestock plays a unique role in agriculture. For instance, cows provide milk and beef, while chickens offer eggs and meat. These animals are essential for various agricultural practices.
Raising livestock supports food security in communities. It offers a reliable source of protein for many families. However, livestock farming has challenges. Overgrazing can lead to land degradation. It’s crucial for farmers to manage pastures sustainably. Additionally, disease management is vital. Illnesses can spread quickly among animals, impacting farmers' income.
The importance of livestock extends beyond food production. They contribute to the economy through job creation. People working in this sector depend on healthy livestock for their livelihood. Yet, ethical considerations in animal welfare are increasingly pressing. Balancing productivity with humane treatment is an ongoing journey for many farmers.

Livestock plays a vital role in the agricultural sector. Various types of livestock contribute to food production and work on farms. Cattle, sheep, goats, pigs, and poultry are the main types. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), livestock provides over 1.3 billion people with livelihoods worldwide. This significant number reflects the importance of animals in agricultural systems.
Dairy cattle contribute significantly to the global economy. They produce milk, cheese, and yogurt. In 2020, global milk production reached about 900 million tons. Additionally, sheep and goats are known for their wool and meat. Studies show that sheep provide essential fiber for many textile industries. On the other hand, pigs are efficient converters of feed into protein. They can utilize a wide variety of feed sources.
However, livestock farming faces challenges. Animal health issues and disease outbreaks can cause significant losses. Overgrazing can lead to soil degradation. The environmental impact of livestock farming is also under scrutiny. Climate change affects livestock productivity. Hence, the industry must adapt and innovate to maintain sustainable practices while meeting global food demands.
Livestock plays a crucial role in farming communities, significantly impacting local economies. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization, livestock accounts for about 40% of global agricultural GDP. This contribution emphasizes the financial weight livestock carries in rural areas. Farmers rely on livestock for income, food, and even cultural identity. In many communities, chicken, cattle, and goats are not just sources of meat; they are part of everyday life.
The economic impact extends beyond the farm. Livestock farming creates jobs in various sectors. Feed production, veterinary services, and meat processing rely heavily on the livestock industry. In fact, a report by the World Bank states that livestock supports the livelihoods of over 1.3 billion people worldwide. Despite this, challenges remain. Rising feed costs and climate change put pressure on farmers. Many struggle to meet basic needs while facing unpredictable market shifts. It's essential to reflect on these issues as they affect community sustainability.
Investing in sustainable practices is vital. Proper management enhances productivity and animal welfare. Yet, many farmers lack the resources for necessary changes. Addressing these gaps will ensure that livestock continues to support farming communities, not just economically but also socially and environmentally. The importance of livestock in agriculture is clear, but the journey toward a resilient future is ongoing.
Sustainable practices in livestock farming are crucial for the environment and food security. These practices focus on minimizing negative impacts while maximizing productivity. Rotational grazing is one effective method. It allows pasture to recover, enhancing soil health. Healthy soil captures carbon and supports diverse ecosystems.
Consider the benefits of incorporating agroecology techniques. Mixing crops with livestock can improve resource use. For instance, livestock can help with pest control while benefiting from crop residues. This synergy not only boosts farm yield but also reduces external inputs like pesticides.
Tips for sustainable livestock farming:
- Always monitor animal health to prevent disease.
- Utilize local feed sources to reduce transportation impacts.
- Engage with community programs to share resources and knowledge.
Mistakes happen in farming. Sometimes, overgrazing leads to soil erosion, affecting future growth. Reflection is key; understanding these issues can guide better practices. Each farm has unique challenges, and adaptability is essential.
Livestock agriculture faces numerous challenges today. A major issue is climate change. Rising temperatures and erratic weather patterns affect feed production. Livestock also contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. This creates a tricky balance for farmers. They must adapt their practices quickly.
Animal health is another concern. Outbreaks of diseases can devastate herds. Vaccination programs help, yet they can be costly. Farmers often struggle to afford the necessary care. Proper nutrition is also crucial for livestock production. However, sourcing quality feed is becoming increasingly difficult.
Future trends point toward sustainable practices. Regenerative agriculture is gaining traction. It focuses on improving soil health and biodiversity. Farmers are experimenting with different grazing methods. Technology will also play a significant role. Precision farming could optimize feed use and reduce waste. Yet, challenges remain in access and costs. The path ahead is complex but essential for a resilient agricultural future.
| Livestock Type | Importance in Agriculture | Challenges Faced | Future Trends |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cattle | Provide meat, milk, and leather | Disease outbreaks, climate change impact | Sustainable farming practices, genetic improvements |
| Sheep | Source of wool, meat, and milk | Predator threats, market volatility | Organic wool production, technological advancements |
| Pigs | High feed conversion efficiency for meat | Waste management, disease control | Indoor farming innovations, breeding strategies |
| Goats | Milk, meat, and land management | Market access for smallholders | Diversification of products, value-added processing |
| Poultry | Egg and meat production | Biosecurity issues, antibiotic resistance | Alternative proteins, welfare improvements |